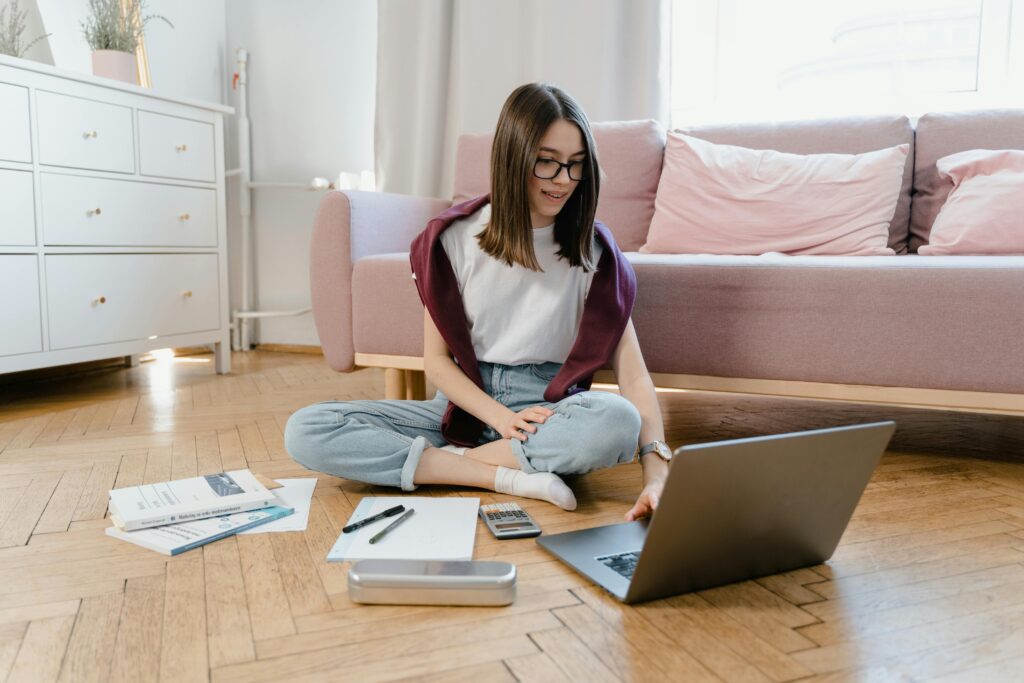
Beyond the Algorithm: Human Jobs Safe from AI in 2025
As artificial intelligence accelerates its march through industries, many workers are left wondering: Will my job survive the rise of machines? While automation is transforming the global workforce, certain roles remain untouched, relying on human empathy, creativity, and nuanced judgment that no algorithm can replicate. These “AI-proof” careers tap into the essence of what makes us irreplaceably human, and they’re thriving even in 2025’s tech-driven world.
Mental Health Workers: Empathy Can’t Be Engineered
While AI can be used for diagnostic tasks and administration in healthcare, it lacks the emotional intelligence to provide compassionate mental health care. On the other hand, a mental health professional possesses empathy, good communication skills, active listening, interpretation, and problem-solving abilities, many of which are inherent to human experience. Thus, mental health care is grounded on profound human connection and subtle understanding of complex emotions, which machines cannot truly replicate. Roles in this sector that are AI resistant include psychologists, counselors, and social workers. Generally, these types of careers require a master’s or doctoral degree, accompanied by certifications or licenses to practice. In terms of earning potential, the mental health field offers ample opportunities, with many practitioners earning salaries exceeding six figures.
Creative Minds: Where Imagination Outpaces Automation
AI tools create art, music, and texts, but they cannot replace the ingenuity and originality of human creativity. Ideas and concepts are something that AI cannot generate in the way a human mind does, and it cannot develop a gripping story (written, visual, or otherwise) grounded in real experiences.
Going AI-proof would be, for example, designers, filmmakers, writers, and marketing strategists. Typically, creative careers require a bachelor’s degree and a very strong portfolio. In the salary department, it can vary enormously, depending on the industry, role, and company for which you work. In general, you would expect to make anywhere in the range of $50,000 to $100,000 annually.
Skilled Trades: Craftsmanship Beyond the Code
AI and robotics can carry out mechanized operations; however, skilled labor requires fine motor coordination and craftsmanship that technology has been unable to render perfectly. In addition, skilled trades involve site-specific problem-solving, along with hands-on technical expertise, which, to this day, has been difficult to imitate. Electricians, plumbers, carpenters, and HVAC technicians are some of those AI-safe occupations. Starting a trade career would require a certificate, an apprenticeship, and then licensure. Trade workers earn anywhere between very different ranges, just like those in the arts, but in time, one can earn a very solid income-close to six figures.
Healthcare Heroes: Compassion at the Core
As we mentioned earlier, AI can help with diagnostics and even managing records, but it cannot replace the compassion and precision needed for patient care. Healthcare involves both technical knowledge and personal skills to meet the needs of patients, who are all uniquely different. This is a job that only humans can do.
If you want a healthcare career that AI cannot take over, think about becoming a surgeon, physical therapist, or radiologist. Most of these jobs need advanced degrees and certifications, but the pay and the satisfaction that come from helping others are more than compensation for the time spent in school. Depending on your specific career, you can earn over $200,000 a year.
Educators & Trainers: Teaching the Human Way
AI can enhance learning with available resources such as customized apps or virtual mentors, but it cannot replace the relationship and flexibility that comes with an excellent educator. Educators have to identify each student’s needs while also ensuring that they remain motivated, along with re-adjusting to how each student learns, respectively. These are attributes that AI does not possess or recognize. Educator careers that are least likely to be impacted by AI are teachers, professors, and corporate trainers. Each education varies, but you will always require a minimum bachelor’s degree in your subject field. Professors usually require a higher degree, and corporate trainers must hold some form of certification. Depending on your position and where you are located, your salary could be $40,000 to $100,000 a year.
Legal Experts: Judgment Beyond the Algorithm
AI can assist in certain aspects of legal research and document review, but it cannot mimic or replace the strategic thinking and advocacy that lawyers and judges provide. The law indeed involves interpreting much finer legal principles and crafting argumentation that is reliant on human judgment. Legal career paths that are AI-proof comprise lawyers, judges, paralegals, and mediators, with the expectation of a juris doctor (JD) degree for almost all of them, except for paralegals, who typically require an associate degree plus certification. As a reminder, averages go all over the place, but their annual salary averages range from approximately $50,000 on the low end to greater than $100,000 on the high end.
Scientists & Researchers: Curiosity That Can’t Be Programmed
AI makes it easier and faster to analyze data across diverse fields, but human curiosity, hypothesis generation, and ethical considerations are all part of scientific discovery. In particular, research is not only about discovering the right answers, but also about asking the right questions and interpreting the results in ways that AI alone cannot reproduce. If you are in search of an AI-proof career in science, you could become a biologist, chemist, data scientist, or environmental researcher. A master’s degree or a PhD is required for most of these careers, depending on the field. Annual salaries will vary depending on your specialization and experience level, but could range anywhere from $60,000–$120,000.
Hospitality Professionals: Personal Touch in a Robotic World
AI can certainly improve efficiency in hospitality, but all jobs involving dealing with the customer directly will hinge on human-centered skills: empathy, adaptability, and cultural awareness. In other words, the interaction that hospitality is all about – anticipating guest needs, rectifying complaints, providing easy solutions, and developing personalized experiences – can’t be done by AI.
Hospitality professions that are not susceptible to AI include hotel management, event managers/planners, chefs, and customer service representatives. Educational requirements for these roles vary widely, but most require at least a bachelor’s degree and some on-the-job training. The overall hospitality sector is quite broad, meaning average salaries will vary. You could find yourself earning around $30,000 per year on the lower end, while other roles could put you near a six-figure income, depending on the role and where you live.
Conclusion
As we stand at the intersection of technological brilliance and human resilience, it’s clear that not all jobs are destined for automation. The roles that require heart, hands, and human insight, whether it’s guiding someone through emotional distress, crafting a story that stirs the soul, or solving real-world problems on the spot, remain essential. In 2025 and beyond, our most secure jobs will be the ones that showcase our most irreplaceable traits: compassion, creativity, judgment, and the innate ability to connect. Rather than fearing the rise of AI, we can embrace it as a tool while safeguarding the careers that speak to our shared humanity.

The Power of Carbs: Why Your Body Loves This Vital Fuel
Carbohydrates have long been misunderstood in popular health trends, often unfairly blamed for weight gain or sluggishness. Yet, the truth is far more nourishing: carbs are a vital source of life-sustaining energy and are essential for both physical and mental well-being. From fueling every breath and heartbeat to supporting digestion, mood, and muscle strength, carbohydrates quietly perform numerous vital roles in our bodies each day. In this article, we’ll uncover the powerful benefits of healthy carbohydrates, dispel common myths, and provide simple guidance on how to meet your daily needs through natural, wholesome choices.
Carbohydrates are a vital macronutrient providing energy for the body. A healthy diet for adults should include 45-65% of daily calories from carbohydrates. Not eating enough carbohydrates can lead to low energy, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
Types of Carbohydrates and Healthy Food Items:
• Simple Carbohydrates
• Sugars: Found naturally in fruits and milk and added to processed foods.
• Healthy examples: Whole fruits, milk.
• Less healthy examples: Sugar-sweetened drinks, pastries, candies
• Complex Carbohydrates
• Healthy examples: Whole grains like brown rice, oats, whole wheat bread, and pasta, starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes and corn.
• Fiber: Found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, beans, and whole grains.
• Beans and lentils, whole fruits and vegetables, especially those with edible skin or seeds, and whole grains.
Benefits of carbohydrates
• Primary Energy Source: Carbohydrates are the body’s main and preferred source of energy, especially for the brain and muscles. When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which is then used as fuel by cells, tissues, and organs. Glucose powers essential bodily functions like breathing, maintaining body temperature, and heart and muscle contractions.
• Stored Energy: If your body has enough glucose for immediate needs, it can store the excess as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use. This stored glucose is crucial during periods of high-intensity exercise or when not getting enough carbohydrates in the diet.
• Muscle Preservation: Carbohydrates help preserve muscle mass. When glucose is scarce, the body may break down muscle protein to create glucose, leading to muscle loss. Consuming adequate carbohydrates can help prevent protein breakdown and ensure the brain has sufficient glucose for energy.
• Digestive Health: Dietary fiber, a type of carbohydrate that is not digested, plays a crucial role in promoting good digestive health. Fiber can be soluble or insoluble. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats and legumes, draws in water, softens stool, and eases bowel movements. Insoluble fiber, found in whole grains and the skins of vegetables, adds bulk to stool and speeds up its passage through the digestive tract, helping to alleviate constipation.
• Heart Health and Diabetes Management: While excessively refined carbohydrates can be detrimental, consuming plenty of dietary fiber benefits heart health and blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber can help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol by binding to bile acids and preventing their reabsorption. Higher fiber intake has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. Fiber also helps delay the absorption of carbohydrates in the digestive tract, leading to lower blood sugar levels after meals and potentially improving blood sugar control, especially in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
• Other Benefits:
Carbohydrates, particularly complex carbohydrates from whole, natural foods, are associated with a lower risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Fiber-rich carbohydrates can contribute to feelings of fullness and satisfaction, potentially aiding in weight management. University of New Hampshire states that complex carbs are a natural pre- and probiotic that feeds the good bacteria in the gut, promoting overall gut health. Some research even suggests that carbohydrates may influence mood, with low-carb diets potentially increasing feelings of anxiety and depression.
Recommended daily carbohydrate intake:
• The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) recommends that carbohydrates comprise 45% to 65% of daily calories. This range is associated with a healthy, balanced diet and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
• For a 2,000-calorie diet, this translates to approximately 225 to 325 grams of carbohydrates per day.
• The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for carbohydrates is at least 130 grams per day for adults, based on the amount needed to provide the brain with sufficient glucose.
• For fiber, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) recommends 14 grams per 1,000 calories, which equates to about 28 grams daily on a 2,000-calorie diet. Most people in the United States do not meet this recommendation.
Tips for Healthy Carbohydrate Consumption:
• Prioritize whole grains: Choose whole grains over refined grains.
• Choose fiber-rich foods: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and legumes in your diet.
• Limit added sugars: Reduce consumption of foods and drinks with added sugar.
Repercussions of not eating enough carbohydrates
- Fatigue and Weakness: Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, and a deficiency can lead to fatigue, weakness, and reduced physical and mental performance. Your body may struggle to find alternative energy sources.
- Brain Fog and Difficulty Concentrating: The brain relies heavily on glucose for fuel. Insufficient carbohydrate intake can compromise neurological function, leading to cognitive deficits like impaired attention, memory issues, and difficulty concentrating.
- Headaches and Dizziness: Low carbohydrate levels can cause fluctuations in blood sugar, potentially triggering headaches and dizziness.
- Muscle Loss: When the body doesn’t have enough glucose from carbohydrates, it can resort to breaking down muscle protein for energy, leading to muscle loss.
- Digestive Issues: A lack of fiber, common in diets restricting carbohydrates, can lead to digestive problems like constipation or diarrhea. Fiber is essential for regulating bowel movements and maintaining gut health.
- Bad Breath: A deficiency in carbohydrates can lead to the body entering a state of ketosis, where it breaks down fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This process produces ketones, which can be released through the breath, causing a distinctive, unpleasant odor.
- Increased Health Risks: Long-term carbohydrate restriction, particularly when replacing carbs with high amounts of saturated fats and restricting the diversity of the diet, can increase the risk of heart disease, certain cancers, and other health issues. Some studies have even linked low-carbohydrate diets to increased mortality, although the evidence is not conclusive.
- Keto Flu: Transitioning to a very low-carb diet can lead to a cluster of temporary symptoms known as the “keto flu,” including headache, irritability, and brain fog.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Restricting fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, can lead to dietary imbalances and potential deficiencies.
Conclusion:
Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet, playing crucial roles in providing energy, supporting brain function, promoting digestive health, and potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, and limit your intake of added sugars and refined grains. While low-carb diets may be suitable for some individuals, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet.

When the Engine Stalls: Reclaiming Health Through Conscious Eating
Feeding Your Body Non-Nutritious Junk Food:
Imagine putting diesel fuel into a gasoline engine- an immediate recipe for disaster. That’s pretty much what we’re doing to our bodies when we load up on a diet full of empty calories. These are the foods that bring little to the table in terms of nutrition, and are packed with sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, yet lacking in essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and protein. Just like an engine that stutters and fails with the wrong fuel, our bodies quietly struggle under the burden of poor eating habits.
1. Fuelling the Body for Optimal Health:
It’s pretty amazing how our bodies can heal and regenerate themselves, as long as we give them the right raw materials. Feeding them the wrong kinds of food can cause damage, even if it happens gradually. Unfortunately, our taste buds often struggle to appreciate what’s truly good for us, which can make it tough to choose wisely.
Revamping our diet isn’t about jumping on the latest trends or punishing ourselves; it’s about getting our internal systems back on track to function smoothly, efficiently, and with energy. A diet rich in nutrients supports everything from our immune system and brain health to emotional stability and long-term disease prevention.
2. Cleaning Up the Diet:
Most modern diets are packed with processed foods that lack essential nutrients, which can weigh us down. These items often come loaded with additives, preservatives, and unhealthy fats, leading to issues like chronic inflammation, metabolic problems, and a weakened immune system. By cutting back on- or completely removing- these harmful foods, especially those high in added sugars, unnecessary refined carbs, and overly processed meals, our bodies can start to heal naturally.
3. Providing the Right Raw Materials:
To truly nourish your body, it all begins with whole, nutrient-rich foods. Think fresh veggies, vibrant fruits, lean proteins, wholesome grains, and healthy fats. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help your cells repair themselves, boost your immune system, and promote overall well-being.
4. The Impact of Poor Choices:
Nutritional needs are something we can’t just overlook. Just like how the wrong fuel can wreak havoc on a car engine, indulging in junk food and sugary drinks can lead to some serious long-term health issues, such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. Our bodies have their limits, and if we keep pushing them, we risk overwhelming their ability to heal and repair.
5. Creating Sustainable Changes:
You don’t have to go all out to switch to a healthier diet. Just take it step by step: start by adding more veggies to your meals, cutting back on sugar, and swapping out processed foods for whole ones. Staying hydrated and keeping an eye on your portion sizes can also make a big difference.
Outro:
True healing begins not with restriction, but with intention. By honoring our bodies with the fuel they were designed to thrive on, we invite balance, vitality, and resilience into our lives. Remember, every small choice you make, every whole food you choose over a processed one, is a quiet act of self-respect. Healing isn’t a finish line; it’s a rhythm we cultivate, one mindful meal at a time. At Healing Assets, we believe your body is your greatest investment. Nourish it wisely.

AI Won’t Replace You - But Someone Using AI Will
Introduction: The Fear and the Future:
Every single time technology makes a leap into the future, an advance is always followed by a wave of fear of change, fear of obsolescence, fear of being left behind. The same is true for Artificial Intelligence (AI). From copywriters to accountants, designers to analysts, professionals from various industries are all concerned with the same question:
Will AI replace me?
Here’s the reality: AI is not your rival. It is not the enemy. But to ignore it might be. Because while AI won’t replace you, someone competent at using AI very effectively might.
Let’s investigate why.
1. AI, the Tool, Is Not a Threat:
The carpenters were not replaced by the hammer. Math was not ended by the calculator. AI is the same- it’s a tool. One with tremendous power, yes. But a tool nonetheless.
AI cannot replicate human intuition or empathy, or lived experience. What it can do is enhance your output, save time, generate ideas, and automate the repetitive so you can focus on the meaning.
Whether it’s smarter writing content, massive analyzing data sets, or producing design drafts, across the board, AI helps humanity go faster and smarter. The threat is not AI itself.
2. The Rise of the Augmented Workers:
It’s failing to adapt to a world where others are using it.
The all-important expert workers of the current age are not only specialists themselves but also acknowledge the growing trend of technology adaptability and AI compatibility in the entire workflow.
We have coined the term augmentation professionals for these: an amalgamation of human creativity and critical thinking, timescale, and speed through AI.
For example:
• Marketer: In minutes, draft campaigns by leveraging AI.
• Analyst: Feeds the numbers into AI tools to find the big trends.
• Writer: Brainstorms faster with AI prompts.
3. Mindset matters more than the skillset:
The art of using AI has nothing to do with being a code master or a technology wizard; it is about having the right mindset.
You do not need to know anything. Just curiosity will do; wanting to try. Ask: What can this tool help me do better, faster, or differently?
So many of the AI tools out there today make it accessible, and you do not have to be a programmer — just open to possibilities.
4. Adapt or Get Left Behind:
The story of history is that people who resist tools generally find themselves surpassed by those who accept them.
Think early about the Internet. Companies that didn’t go online perished. This is now beginning to repeat itself with AI.
You do not need to use every AI tool that exists, but you will need to be aware of its possibilities – and to start incorporating what does apply to you or your work.
Having nothing to do with it is risky. Not because AI is taking over, but because someone else will not hesitate to adapt to it.
5. How to Start Using AI …Today:
There’s no need for you to set yourself a five-year plan. All that is required is taking the first step. Here are a few pointers that can help you take action:
• Trying out some tools such as those examples: ChatGPT, Notion AI, or Canva’s fabulous AI design features.
• Automating small tasks: calendar scheduling, drafting emails, summarizing documents
• Learning resources, including YouTube, LinkedIn Learning, and Medium.
• Work with AI rather than against it: Use it as a tool to augment your strengths rather than going toe-to-toe with your greatest competition.
Start where you are. Use what you have. AI is not replacing creativity, but it’s supercharging that.
6. Those Human Characteristics Still Matter Most:
AI can speculate, process, and analyze, but it cannot truly feel.
Empathy, storytelling, ethical judgment, leadership – these are all very human qualities. AI can assist, but never replace them.
In the future, the best professionals will not be the ones who are resistant to the technology, nor will they be those who rely on everything it has to offer. They will be those who marry intelligence of either kind, artificial and emotional, to create something larger.
Conclusive Thoughts:
Partner With Progress: Partner with AI:
Not the tools nor the algorithms, but the future is for those who know how to make use of intelligent systems.
So, don’t fear Artificial Intelligence – learn to collaborate with it. Find out what it can enhance, and where your unique edge truly lies.
Because AI will not replace anyone, but someone with AI can.
And that someone could be you.

Trade Tariffs and Economic Repercussions:
Tariffs and drastic changes to trade policies are some methods governments use to serve economic or political ends. While such policies may give short-term benefits to certain industries, the long-run cost is extended and difficult for the larger economy. Such policies lead to higher consumer prices, disruptions in global supply chains, and slower economic growth; each presents businesses, consumers, and governments with varied problems.
Trade Tariffs Cause a Rise in Prices:
A tariff is one of those taxes that will most immediately start to show an effect on rising consumer prices. Since tariffs are taxes on imported goods, upon levying them, the cost of goods will automatically go up. Forced to absorb the higher cost, if they can, businesses needing the imported goods and products will take a hit on lowered profits, which may be just too much for them to take. Usually, of more importance to the common consumer wanting that shiny new electronic device, stylish clothes, or a mouth-watering dish, the hike in prices of these products after levying a tariff, then affects directly the purchasing power of the consumer.
Tariffs Disrupt Global Supply Chains:
The liquidity of raw materials and components worldwide is vital for many industries—for example, electronic companies import semiconductors. Trade tariffs, which impede a supply chain, become relevant when they raise the costs of goods and extend the time of goods’ transfer over borders. In turn, this causes inefficiencies and shortages, as well as increases in adjustment costs, which companies incur while looking for alternative sources of supply or making changes in their processes. Uncertainty breeds further disruption, where companies start re-evaluating their long-term strategies and possibly avoiding making any investments due to trade policy uncertainty.
Tariffs Provoke Retaliatory Measures and Trade Tensions:
In retaliation, tariffs often provoke countermeasures from other nations, culminating in trade wars. For example, if one country imposes tariffs on foreign cars, the country affected by these tariffs may retaliate by placing counter-tariffs on the exporting state’s agricultural products, such as soybean or wheat. Such retaliatory acrimony affects the flow of goods and raises the costs of doing business for industries on both sides. Beyond economic damage, retaliatory tariffs are detrimental to international relations and erode the ability of governments to trust one another and work together in the future. Such damage to diplomatic ties may also have long-term effects, such as laying the way for difficult trade negotiations in the future.
Tariffs Reduce Economic Growth:
Rising prices and supply chain disruptions combined with retaliatory tariffs slow down economic growth overall. With tariffs pushing up production costs, companies may opt to curtail production, curtail investments, or postpone expansion plans. Such cutbacks lead to job losses and an attendant reduction in economic activity. Trade policy uncertainty also discourages both domestic and foreign investments, as in the mind of an entrepreneur or an investor the less stable the market conditions, the more uncertainty is warranted. The combination of high-cost trade and uncertainty works to weaken economies, particularly smaller or emerging ones that are overly dependent on exports.
Long-Term Global Consequences of Imposing Trade Tariffs:
Customs duties do protect specific domestic industries for some short-term temporal benefit; all in all, they are detrimental in the longer run. In this modern and ever-connected world, barriers to trade and tariffs primarily lay hindrances in the paths of innovation, efficiency, and competition that would otherwise favor global wealth. Such protectionist policies tend to gravitate toward economic isolationism, in which nations give preference to nurturing domestic industries, coming at the cost of international cooperation. Such attempts could lead to a band-aid global trading system that frustrates efforts in tackling global issues, from climate change to pandemics and eventually to technology.
Conclusion:
As much as tariffs and changes in trade policy may provide short-term benefits, they often bring higher consumer prices, disruption of supply chains, retaliation, and slower economic growth. Policymakers must, therefore, weigh such measures against their long-term effects to avoid hurting the very sectors they intend to protect and to ensure global economic stability.

Comparing the Best Investment Options: Precious Metals, Stocks, or Real Estate?
The debate about which investment is best—precious metals, stocks, or real estate—isn’t new to investors. Each asset class has advantages and risks, and the best fit depends on individual financial targets, risk appetites, and market conditions.
Precious Metals as an Investment:
For hundreds of years, people have treasured precious metals; gold, silver, platinum, and palladium are often considered hedges against inflation and are sometimes viewed as a haven during an economic storm. The greatest appeal comes from their intrinsic value: they’ve always had a worth when fiat currencies and markets fall. Prices fluctuate wildly, though, due to geopolitical occurrences, supply and demand altering conditions, or market speculation. Precious metals don’t pay dividends or rental yields, for instance; profits from them are made only with risky price increases.
Stocks As an Investment: Growth and Income Potential:
Growth potential and income from dividends are the two reasons that stocks are considered one of the most popular investment vehicles. Stocks represent ownership in a company, and for well-established companies or diversified stock indices such as the S&P 500, greater returns have usually been expected over time. Stocks are highly liquid, with buying or selling typically achievable in a day. However, stocks also suffer from volatility, as factors like company performance and economic conditions can lead to drastic changes in value.
Investment in Real Estate: Stability and Tangibility:
Real properties are generally regarded as excellent long-term investment opportunities. Over time, probable values are expected to grow, especially in areas with high demand, while giving owners a steady source of cash flow from rental income. The significant thing about real estate is that it offers ‘security’ to an investor in that it provides it with a certain form of asset. Its appreciation over time is caused by various factors like urbanization and economic growth. However, real estate tends to be less liquid than stocks. Properties may be sold or bought over weeks to months, and high commissions, taxes, and maintenance costs are involved in such transactions.
Comparing the Three Investments:
• Risk and Volatility: Precious metals are typically volatile in the short term but can be very safe havens at other times. Stocks also usually experience less volatility over long-term horizons using diversification. Real estate is more stable but still susceptible to interest rates and local market conditions.
• Liquidity: Among all asset forms listed in this article, stocks have the highest liquidity, precious metal is next to it and at the bottom of this scale comes paid-up real estate.
• Hedge Against Inflation: Precious metals, particularly gold, serve as direct hedges against inflation. Real estate also holds its own in inflationary periods, while stocks may falter.
Conclusion:
There is no one answer for every situation. Stocks provide growth and income, while real estate adds stability through rental income and precious metals can be brought into play during tough economic times. Many investors will choose to take a diversified position among these three asset classes to balance risk and reward according to their particular financial situation.

Here’s How I Learned that Debt is Cheaper Than Equity
During my years working with businesses and banks, I saw a recurring misunderstanding: many founders overlooked how affordable debt could be. That experience inspired me to break it down in this article
In corporate finance, it is a continuous effort for companies to raise funds for operations, expansion, and investment. The two well-known ways of raising capital are debt and equity. Both methods have their merits and demerits; however, debt is generally cheaper than equity. This article aims to explain this phenomenon by examining the cost of debt versus equity, the effects on the financial structure of the company, and the reasons that tend to favor debt for companies aiming to reduce capital costs.
1. Reduced Cost of Capital in Debt Financing:
• The interest rates on debt are usually lower than the returns equity investors require.
• In a liquidation scenario, lenders accept lower returns since debt is considered less risky, and its repayment—both in timing and amount—is more certain.
2. Tax Benefits (Tax Shield) of Debt over Equity:
• Interest payments on debt are tax-deductible, reducing taxable income and effectively lowering the cost of borrowing.
3. Predictable Cash Flow Commitments in Debt Financing:
• Debt financing requires fixed periodic repayments, providing companies with better cash flow control.
• Equity financing, on the other hand, involves variable discretionary dividend payments that may become increasingly costly over time.
4. Absence of Ownership Dilution in Debt vs Equity:
• Financing through debt does not dilute ownership, whereas issuing additional shares reduces control and dividend income for existing shareholders.
5. Lower Issuance Costs of Debt Compared to Equity:
• Issuing debt is generally cheaper as it involves lower administrative, regulatory, and underwriting costs compared to equity.
6. Priority in Claims: Why Debt Has an Edge Over Equity:
• Debt holders rank ahead of equity investors in bankruptcy, making debt a safer option that allows for lower borrowing costs.
7. Retention of Control Through Debt Financing:
• Lenders do not acquire ownership or voting rights, unlike equity investors, preserving the company’s strategic and operational control.
Conclusion:
These advantages make debt a more attractive financing option than equity under normal circumstances. However, excessive reliance on debt can increase financial risk. Therefore, firms must prudently balance their capital structure.

Important Health Benefits of Fasting, Evidence-Based:
Fasting has been used for a thousand years, mainly for religious, cultural, and health reasons. Modern studies show that fasting improves metabolism, brain function, and longevity. Eight science-affirmed healthy benefits are discussed.
1. Blood Sugar Regulation and Insulin Sensitivity:
It has been confirmed that by fasting, blood sugar is normalized, insulin sensitivity improves appreciably, and the risk of type 2 diabetes decreases. Intermittent fasting decreases fasting blood sugar by 3% to 6% and up to 20% to 31% in insulin level for individuals with prediabetic blood glucose, according to a study published in “Translational Research” (Varady et al. 2010). This allows cells to utilize glucose more efficiently by diminishing insulin resistance, which offers a buffer for dangerous spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels.
2. Reduction of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress:
Chronic inflammation plays a critical role in the progression of numerous diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and even cancer. Studies propose that fasting lowers C-reactive protein (CRP) and pro-inflammatory cytokines as inflammatory markers (Moro et al., 2016). By enhancing autophagy, fasting enhances the recycling of damaged cells through the reduction of oxidative stress, which is otherwise a key contributor to aging and diseases
.
3. Fasting lowers the Risk of Heart Disease:
Fasting, which provides various cardiovascular markers, lowers the risk of heart disease. Studies show that intermittent fasting may occasion:
• Decreased overall cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol)
• Lower triglycerides
• Improved blood pressure and arterial function
The “Cell Metabolism” study found that intermittent fasting lowered blood pressure by 6% and improved heart rate variability, one of the important attributes of heart health (Mattson et al., 2017).
4. Neurological Activity:
Fasting stimulates the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a key protein in cognitive function, learning, and memory. Intermittent fasting was shown in a study done in Nature Communications to boost the production of BDNF, which protects against both Alzheimer’s and PD (Alirezaei et al., 2010). Fasting also enhances autophagy in the brain, leading to the disposal of damaged proteins that contribute to neurodegeneration.
5. Fasting Supports Weight Loss and Fat Burning:
One of the well-recognized benefits of fasting is its effectiveness in weight loss. By reducing food intake and boosting metabolic processes, fasting promotes fat burning at an efficient rate. Fasting raises the level of the hormone norepinephrine, which encourages the breakdown of fat, and it boosts the production of ketones, placing the body in a fat-burning mode.
A study published in Obesity found that intermittent fasting resulted in a 3–8% reduction in body weight over 3–24 weeks, making it an effective weight-loss strategy (Catenacci et al., 2016).
6. Elevated Growth Hormones:
Fasting can noticeably elevate human growth hormone (HGH) levels, which is important in muscle development, fat metabolism, and tissue repair. Studies show that the levels of HGH during fasting can increase by 200-500%, causing muscle preservation and fat breakdown (Ho et al. 1988)
.
7. Increases Longevity and Delays Aging:
Fasting has been shown to prolong life in animals by activating cellular repair mechanisms (such as autophagy) and reducing oxidative stress. Among these studies, one study published in Nature showed that in rodent study fasting increased average lifespan by 36-83%, suggesting that fasting may increase longevity in large mammals as well (Fontana et al. 2010)
.
8. It May Help Lower the Chances of Cancer Occurrence while Complementing Cancer Treatment:
Studies point out that fasting may inhibit tumor growth through diminished insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) hormone circulation, which is causally implicated in cancer development. As a result of fasting, chemotherapy may be more effective at pulling off cancer cells while leaving normal cells unharmed (Raffaello et al. 2008).
Conclusion:
Fasting can provide a plethora of health benefits, ranging from enhanced metabolic processes and heart health to the enhancement of brain function and longevity. More human studies are still warranted to be conducted; however, preliminary results would suggest that fasting could alter disease development and enhance health altogether.
CAUTION:
It would be wise to consult a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes

Valuable tips to keep your brain healthy and young:
Organ that at once encompasses all bodily functions, emotions, thoughts, and behaviors is said to be the brain; it is also said to be the most complex part of the human body. The brain weighs three pounds, and it is the tool for intelligence and for interpreting all the senses, and from there, it initiates body movement and controls all behavior. It is within its bony shell and washed by the protective fluid that all these qualities thrive and define us to be the true users of our brains. To ensure it remains healthy, follow these essential tips.
Here are 10 tips to keep your brain healthy:
A 2,000-page dissertation could just cover these initial 10 points to keep the brain healthy.
1. First, eat a healthy diet:
Whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein should be the staples. Processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars you should really avoid.
2. Engage in physical activity:
Regular working out increases the blood flow in the brain. It creates an optimal environment for the growth of new brain cells.
3. Get enough sleep:
You need at least 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Deep sleep is, after all, important for brain function and memory consolidation.
4. Challenge your mind:
Put your mind to the test with things such as new languages, puzzles, or reading really great books.
5. Manage stress:
Meditation, yoga, or a few minutes in nature can all help relieve stress.
6. Stay connected with your social networks:
Social interaction reduces stress and enhances cognitive function.
7. Protect your head:
Always wear a helmet while biking and put on your safety belt.
8. Limit your alcohol intake; don’t smoke:
Excessive use of alcohol and smoking harms brain health.
9. Manage your blood pressure and blood sugar levels:
High blood pressure and diabetes often heighten the risk of cognitive impairment.
10. Annual examinations:
Regular visits to the doctor, for instance, can pick up potential health issues early on.
Conclusion:
Taking these proactive steps can help maintain a healthy, youthful brain and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
CAUTION:
This communication is for informational purposes only. Always consult your physician with any concerns regarding treatment or diagnosis.
About Me
Hi, I’m Amina Phillips! Welcome to my blog!
With a strong background in finance and writing, I’m passionate about sharing practical insights that are easy to understand and apply. My goal is to make complex topics accessible, helping you make informed decisions with confidence. Whether it’s finance, health, or personal growth, I provide content that empowers you. I’d love for you to be part of this journey—feel free to reach out with any questions.
Thank you for stopping by!